Drugs (or any molecules) could be delivered
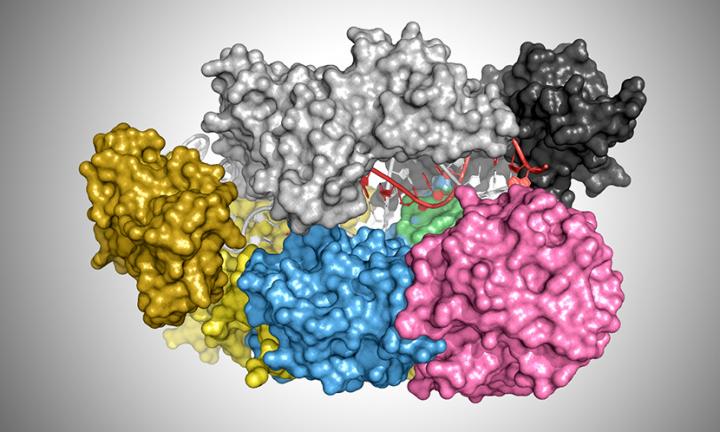 |
| CRISPR Cas12a |
James Collins, MIT, Cambridge used CRISPR to deliver drug molecules. They used water-filled polymers that are
held The Cas12a enzyme can be programmed severs
This property allowed the researchers to build a series of
CRISPR-controlled hydrogels containing a target DNA sequence and single strands
of DNA, which breaks up after Cas12a recognizes the target sequence in a
stimulus. The break-up of the single DNA strands triggers the hydrogels to
change shape or, in some cases
The team created hydrogels programmed to release enzymes,
drugs. the drugs are loadedwas held
 |
| CRISPR cas12a is used to |
References:
1. English, M. et al. Science 365, 780–785 (2019).
Like and follow Layman's Biology for more news on gene editing.